Graph of $y=|f(x)|$
Graphs of $y=|f(x)|$
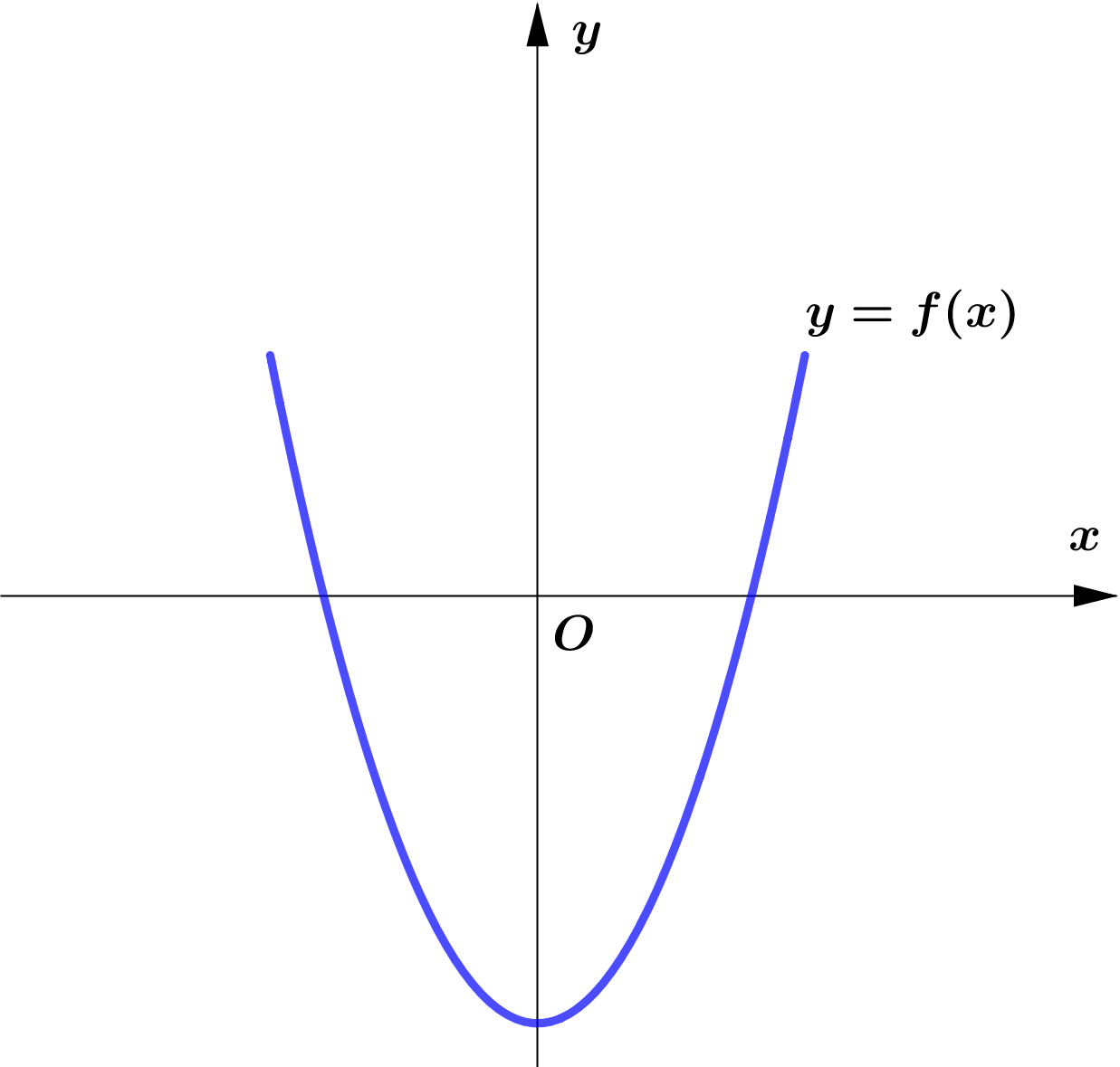
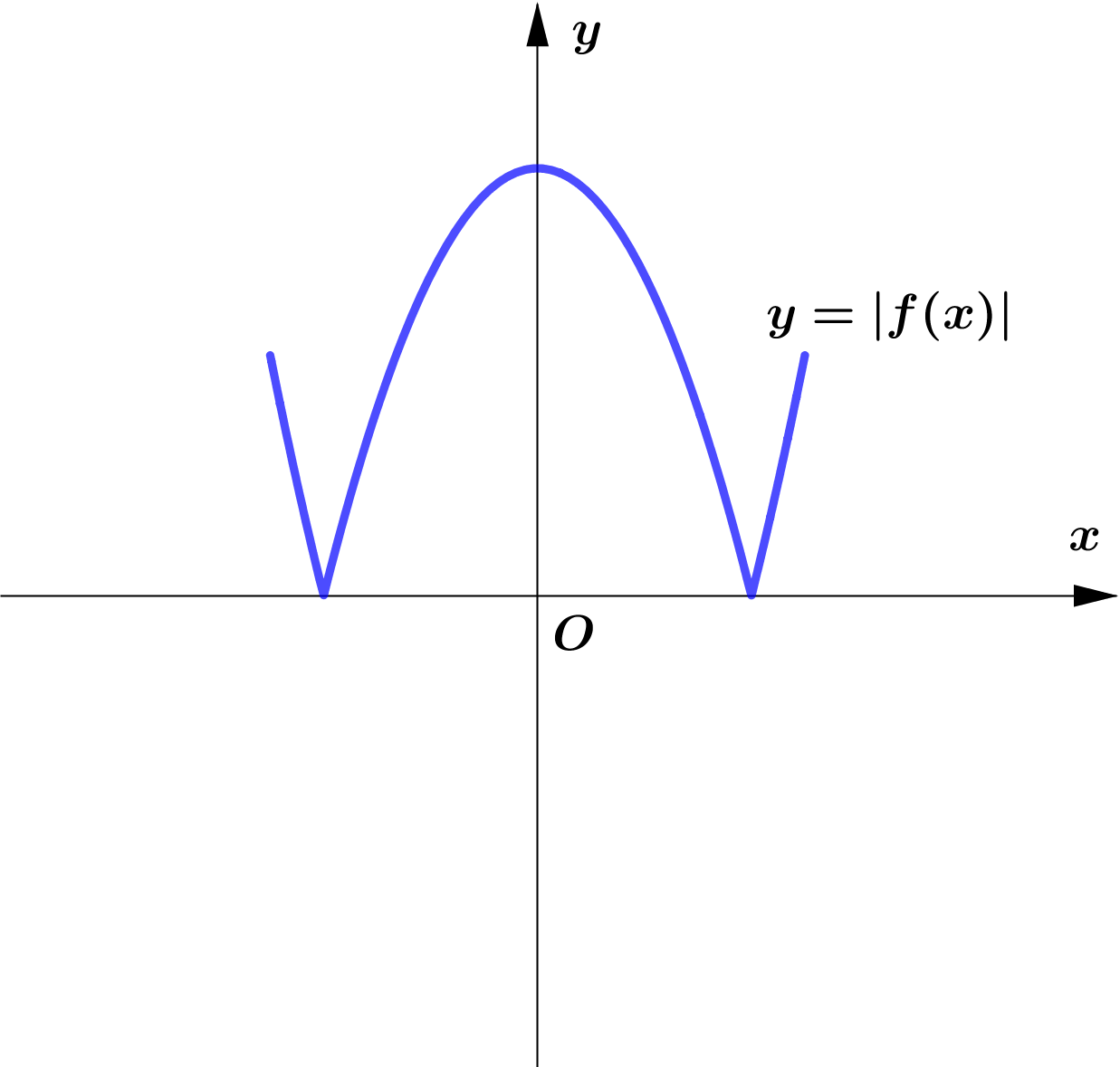
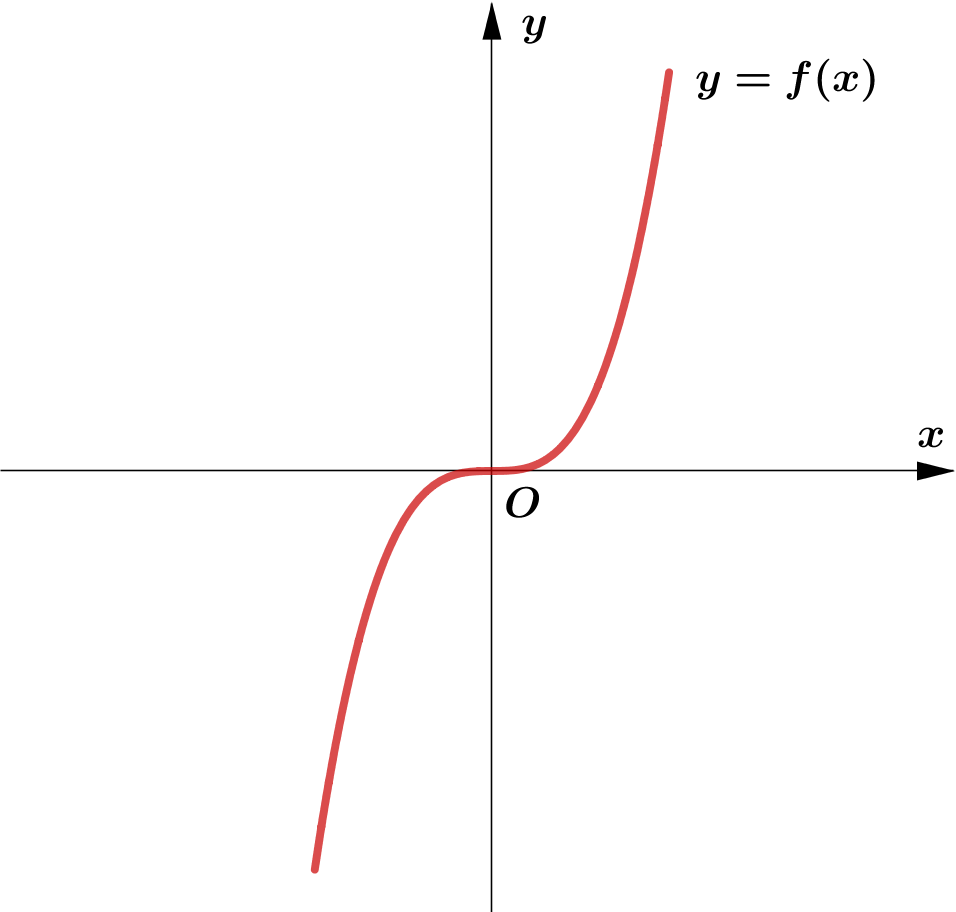
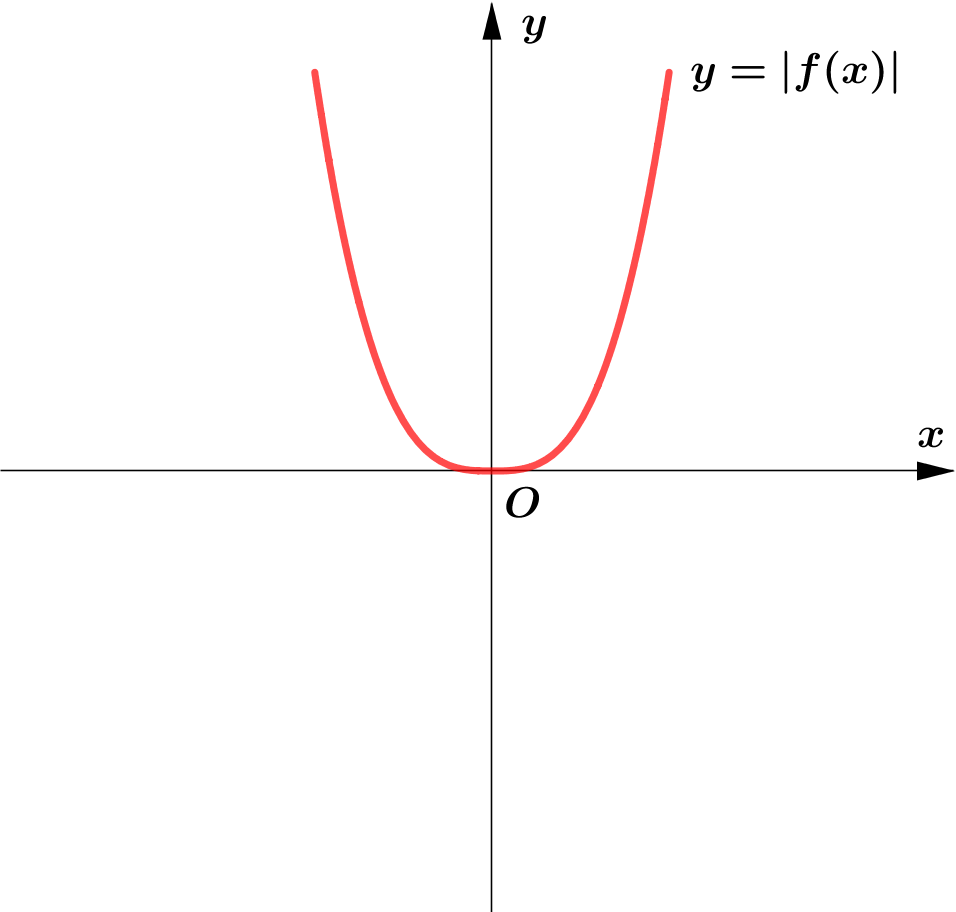
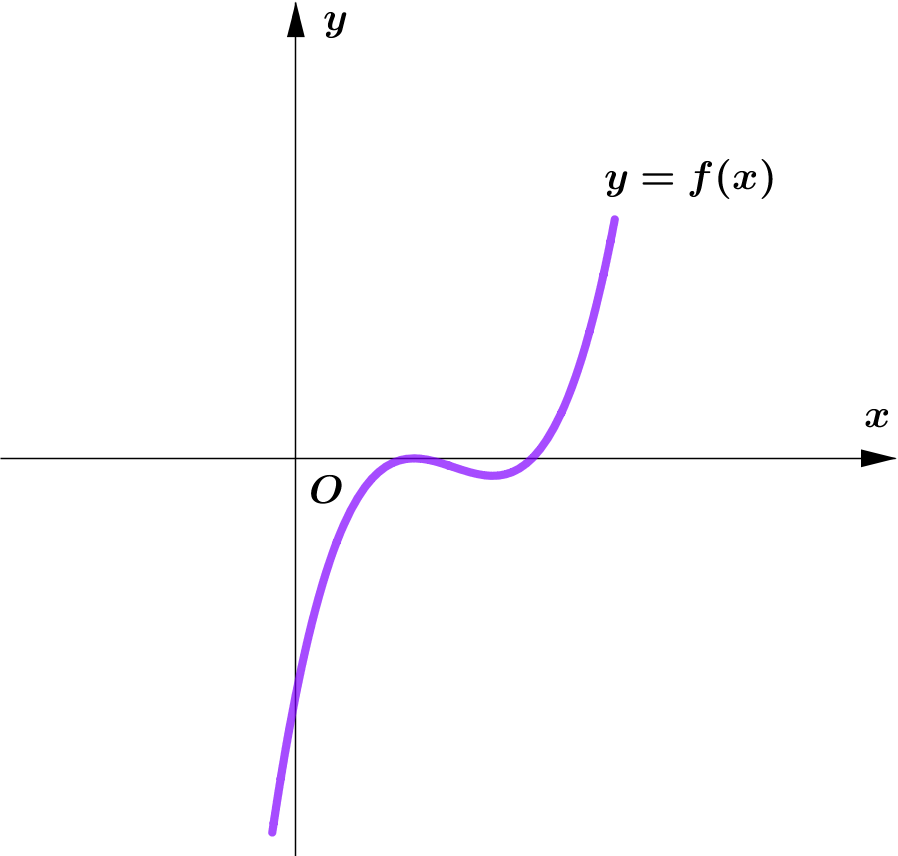
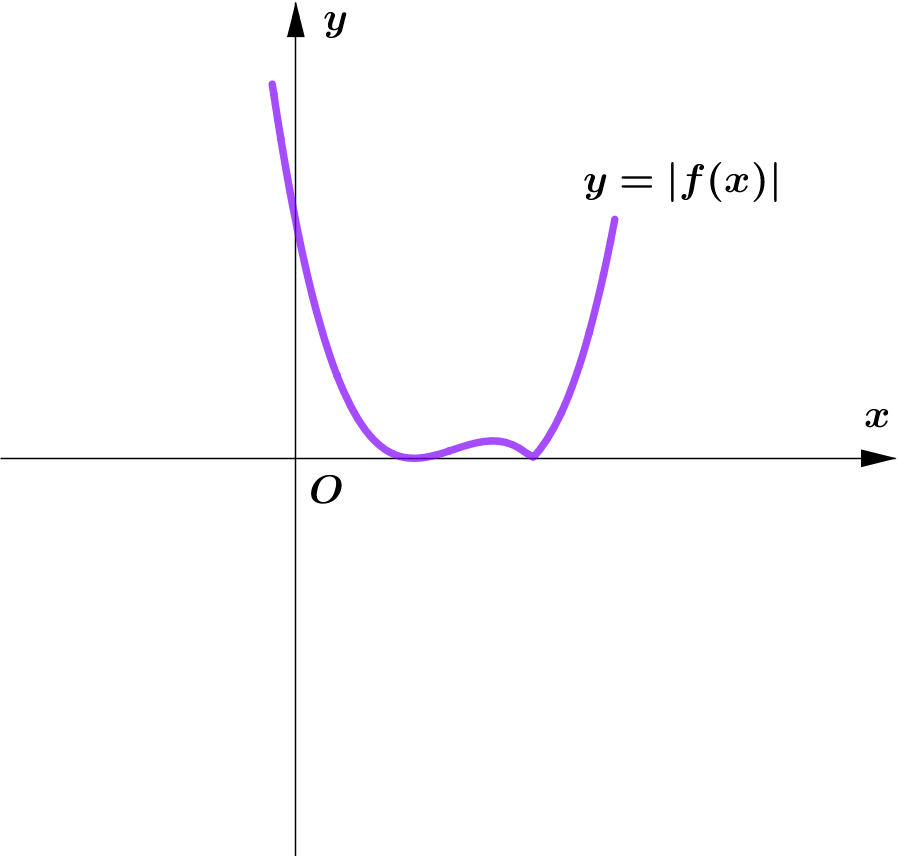
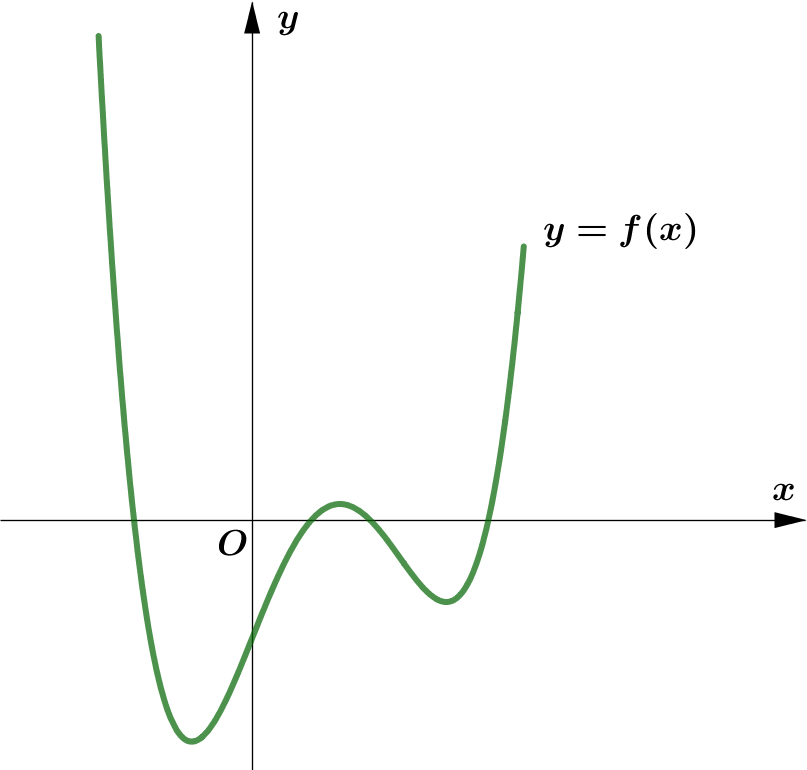
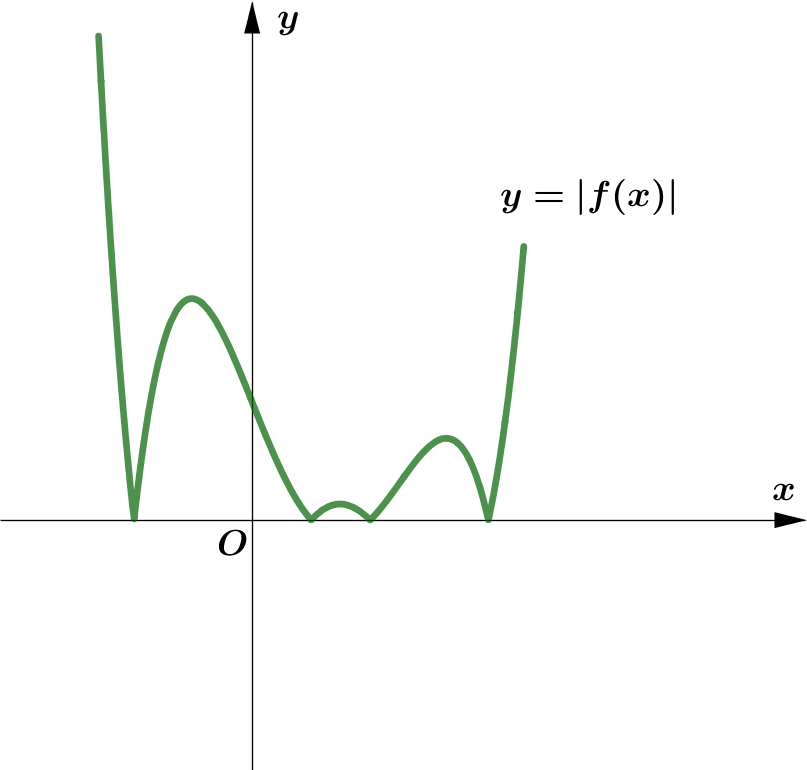
Modulus Function တစ်ခု၏ image (output) များသည် $0$ သို့မဟုတ် $0$ ထက်အမြဲကြီးကြောင်း သိရှိခဲ့ပြီး ဖြစ်သည်။
ထို့ကြောင့် Function တစ်ခု၏ modulus grph ကို sketch လုပ်သည့်အခါ မူလ (parent) Function ၏ $x$-axis အောက်ရှိ
graph ၏ အစိပ်အပိုင်းများကို $x$-axis နှင့် ခေါက်ချိုးညီ $x$-axis အပေါ်သို့ ရွှေ့ပေးလိုက်ခြင်း (reflection about $x$-axis)
ဖြစ်သည်။
Graph တစ်ခုလုံးကို reflect လုပ်ခြင်းမဟုတ်ပဲ Negative Portion ကိုသာ ရွှေ့ပေးခြင်း ဖြစ်သည်ကို သတိပြုရပါမည်။ အောက်ပါ ဥပမာများကို
လေ့လာကြည့်ပါ။
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Question 1
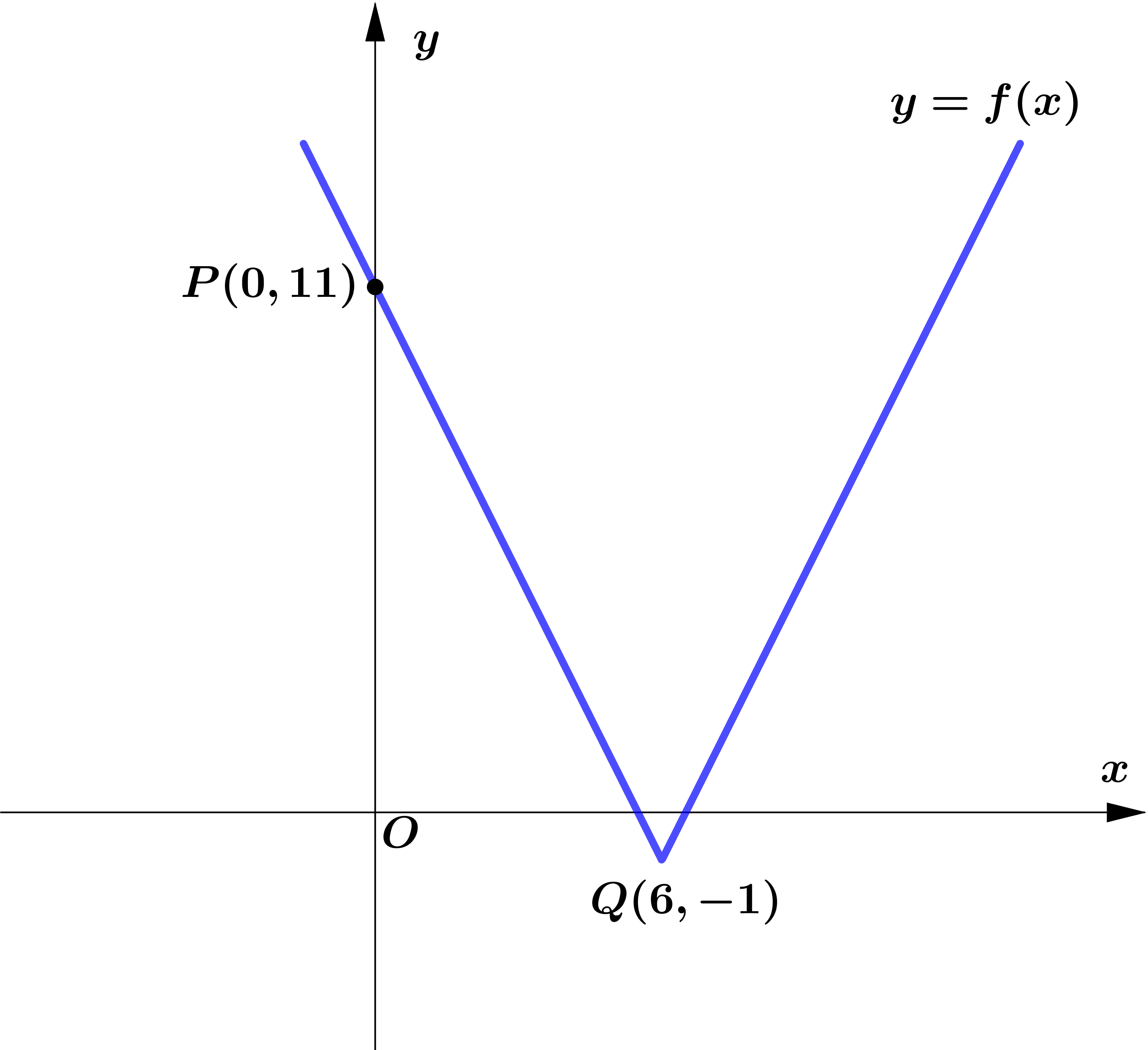
Figure 1 shows part of the graph with equation $y=f(x), x \in \mathbb{R}$.
The graph consists of two line segments that meet at the point $Q(6,-1)$.
The graph crosses the $y$-axis at the point $P(0,11)$.
Sketch, on separate diagrams, the graphs of
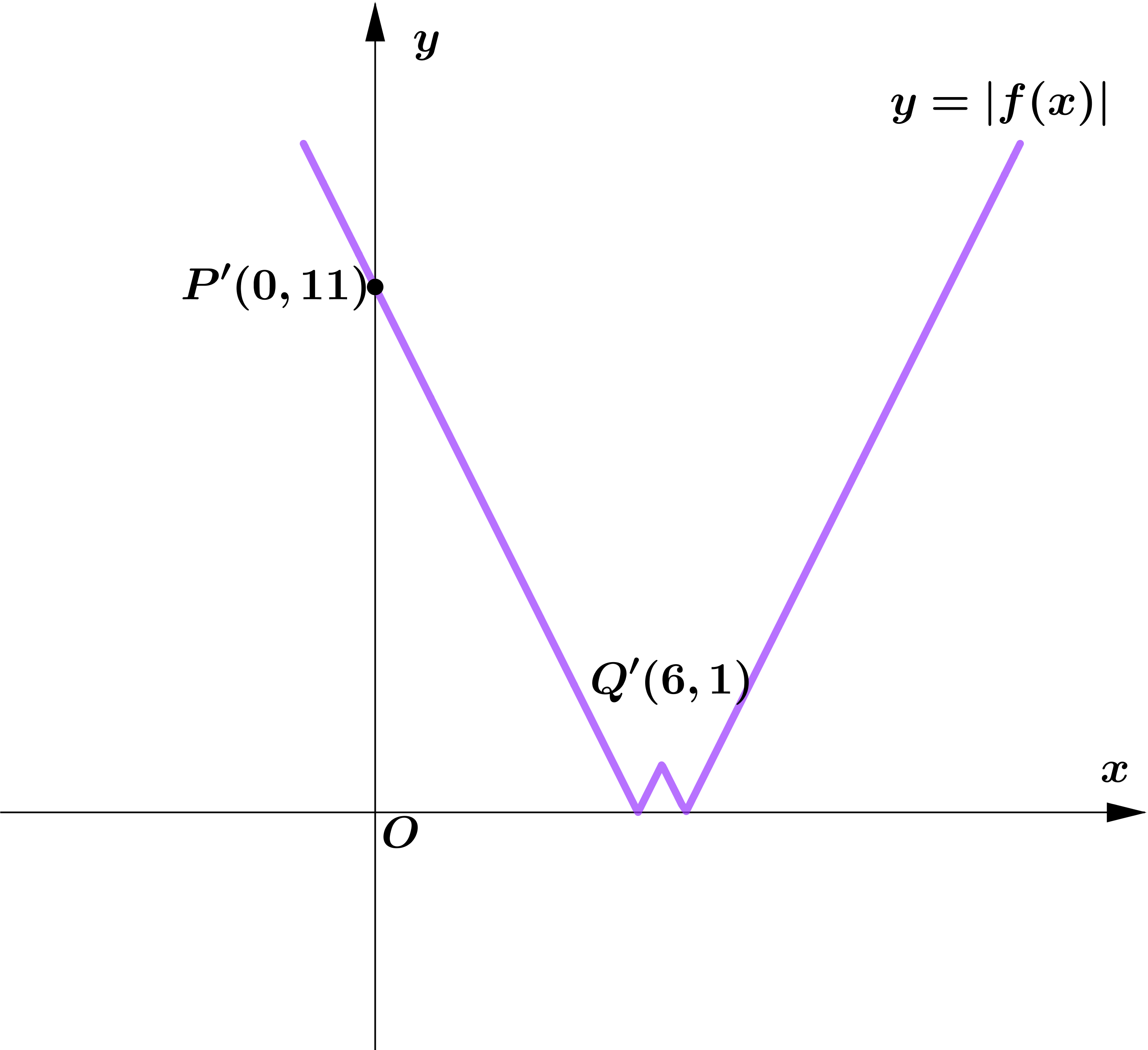
(a) $y=|f(x)|$
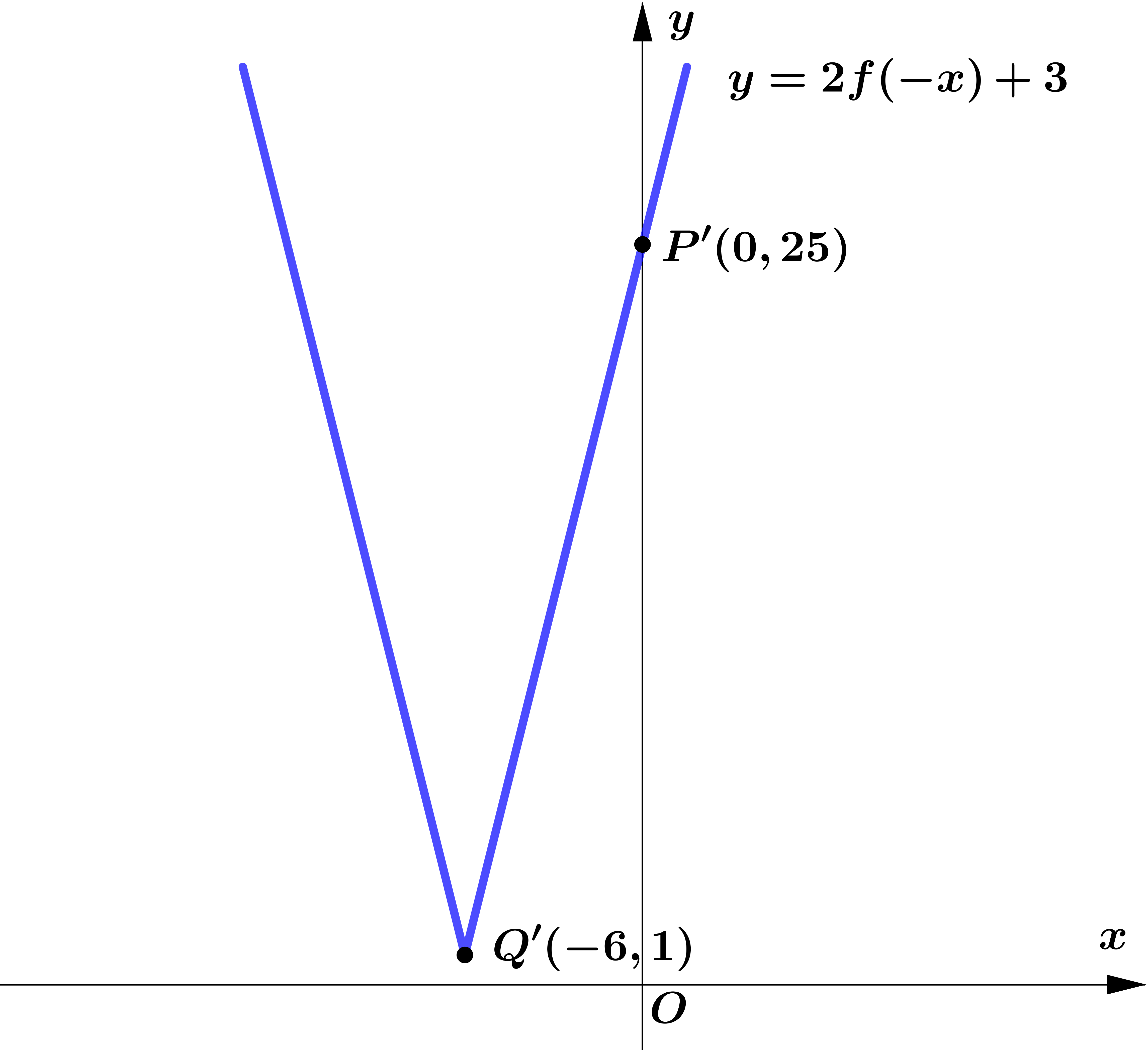
(b) $y=2 f(-x)+3$
On each diagram, show the coordinates of the points corresponding to $P$ and $Q$.
Given that $f(x)=a|x-b|-1$, where $a$ and $b$ are constants,
(c) state the value of $a$ and the value of $b$.
(a) On the graph $y=|f(x)|$.
The point $P$ is unchanged.
The mapped point of $Q$ is $(6, 1)$.
(b) On the graph $y=2f(-x)+3$.
$P(0,11)\rightarrow P'\left(0, 2(11)+3\right)=P'\left(0, 25\right)$
$Q(6,-1)\rightarrow Q'\left(-6, 2(-1)+3\right)=Q'\left(-6, 1\right)$
(c) $\ f(x)=a|x-b|-1$
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\therefore\quad & (b, -1)= (6, -1)\\\\
& b=6\\\\
\therefore\quad & a|0-6|-1 = 11\\\\
& a=2
\end{aligned}$
Question 2
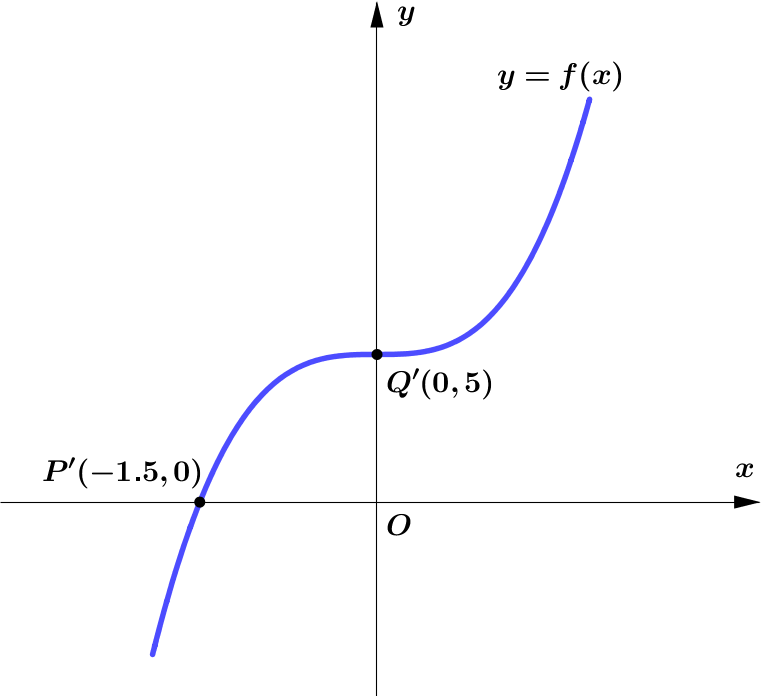
Figure 2 shows part of the curve with equation $y=f(x)$.
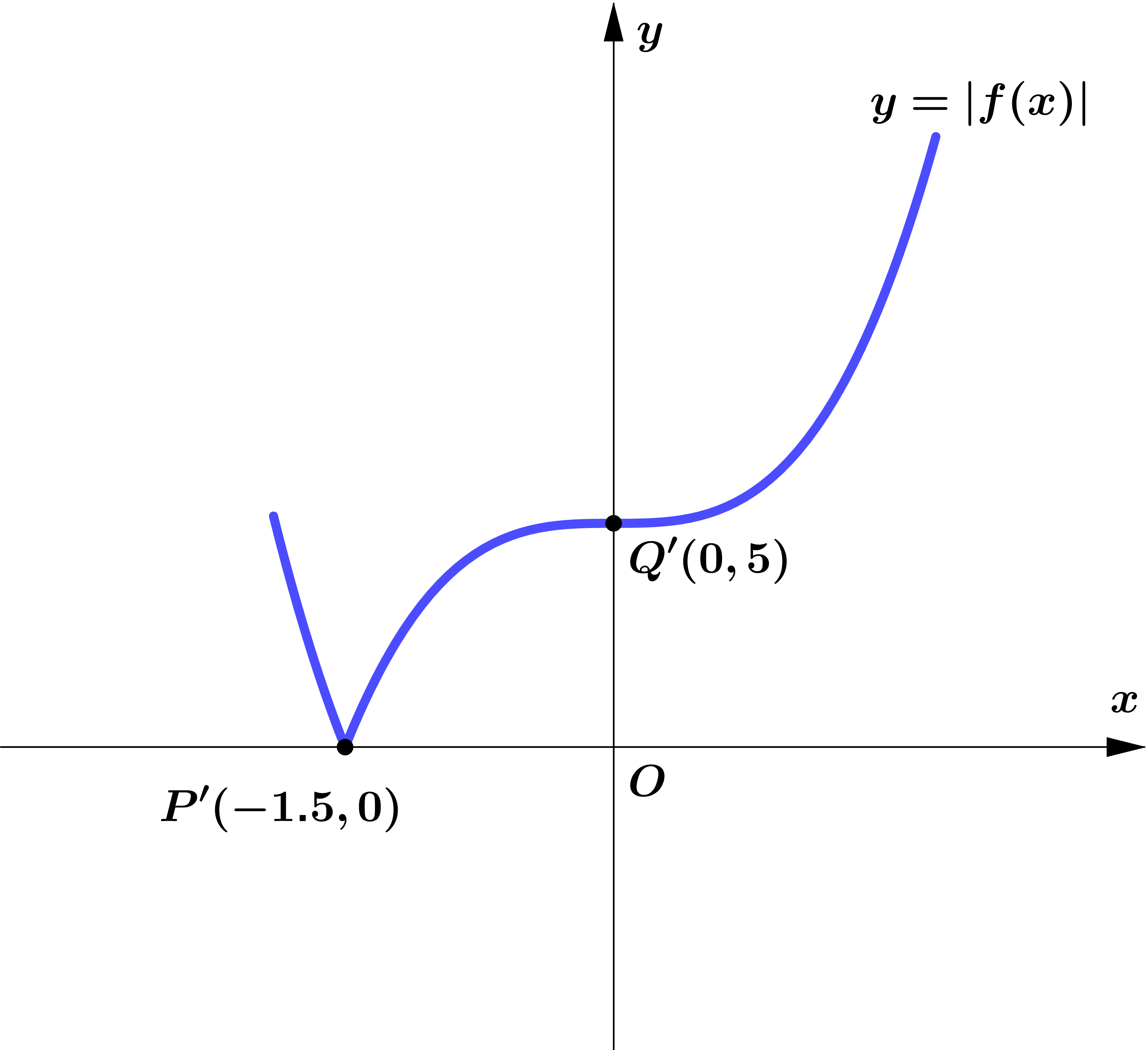
The curve passes through the points $P(-1.5,0)$ and $Q(0,5)$ as shown.
On separate diagrams, sketch the curve with equation
(a) $y=|f(x)|$
(b) $y=2f(3 x)$
Indicate clearly on each sketch the coordinates of the points at which
the curve crosses or meets the axes.
(a) On the graph $y=|f(x)|$.
The coordinates of both points $P$ and $Q$ are unchanged.
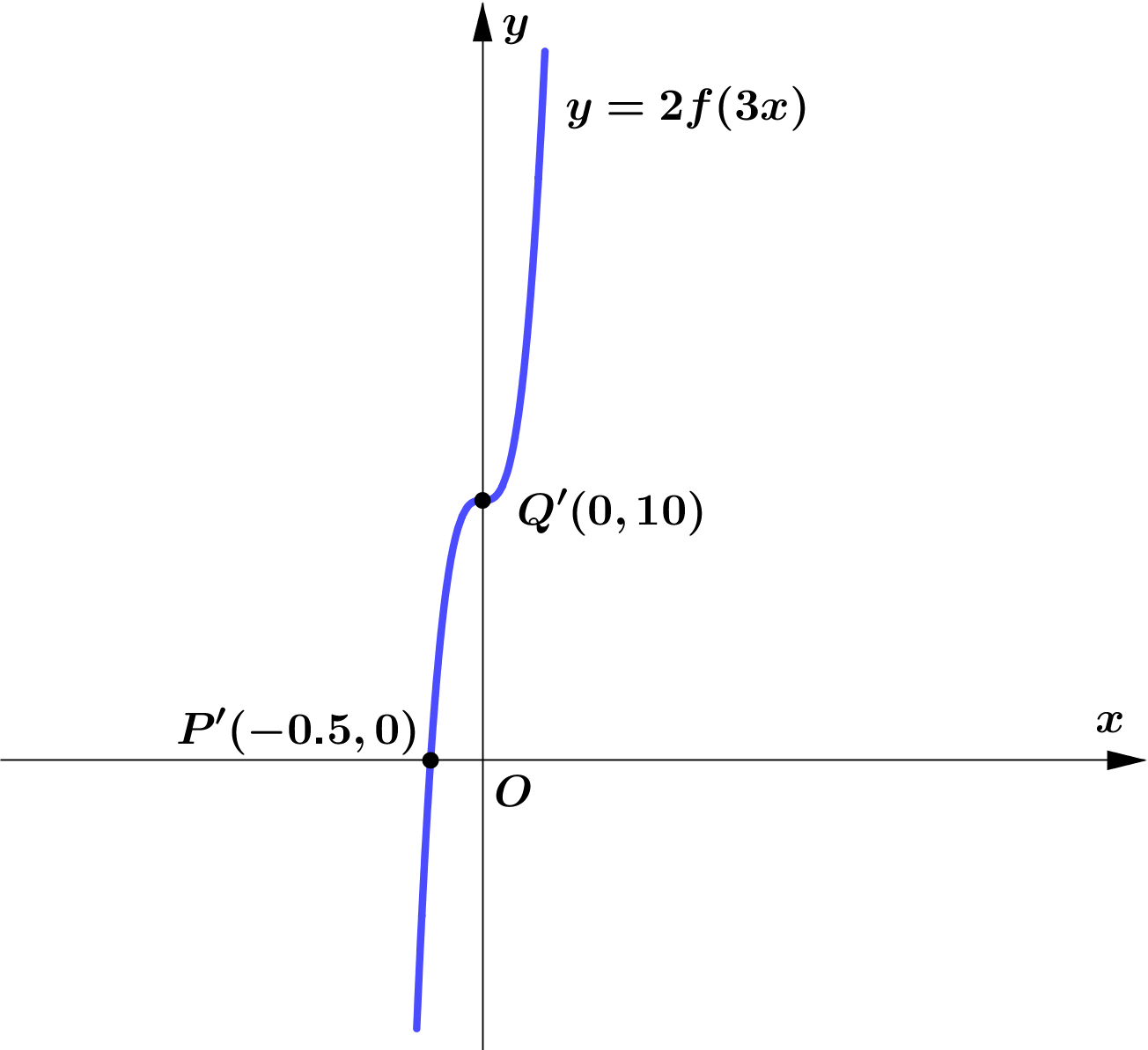
(b) On the graph $y=2f(3x)$.
$P(-1.5,0)\rightarrow P'\left(\dfrac{-1.5}{3}, 2(0)\right)=P'\left(-0.5, 0\right)$
$Q(0,5)\rightarrow Q'\left(0, 2(5)\right)=Q'\left(0, 10\right)$
Question 3
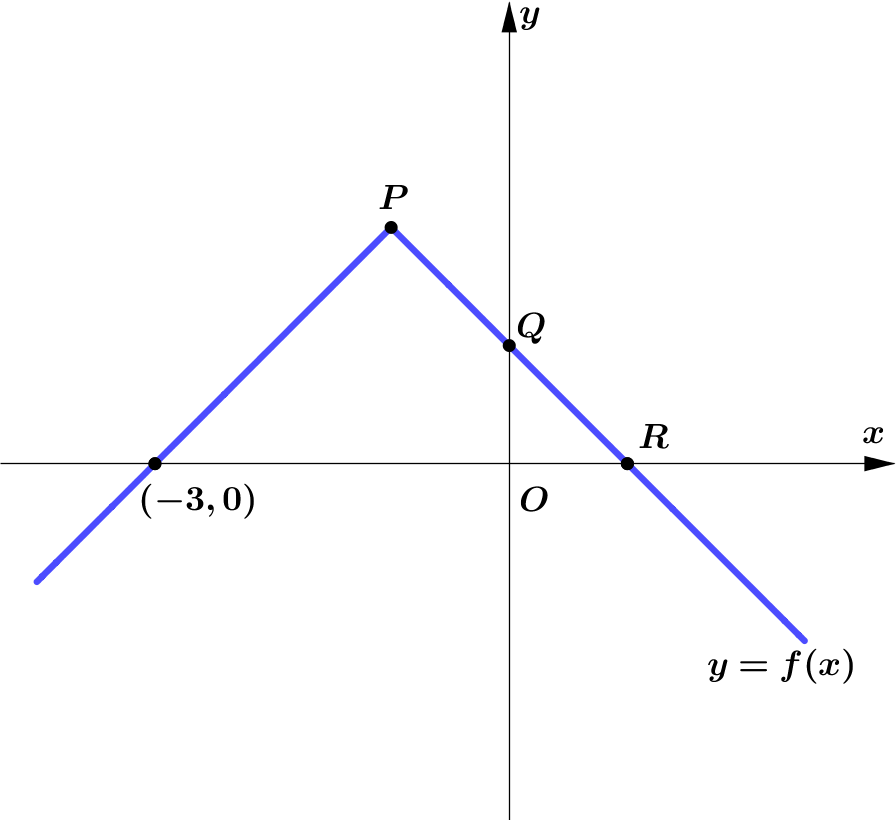
Given that $f(x)=2-|x+1|, x \in \mathbb{R}$.
Figure 3 shows the graph of $y=f(x)$.
$P$ is the vertex of the graph.The graph cuts the $y$-axis
at the point $Q$ and the $x$-axis at the points $(-3,0)$ and $R$.
(a) Find the coordinates of the points $P, Q$ and $R$.
Sketch, on separate diagrams showing the corresponding vertex, $x$ and
$y$-intercepts, the graphs of
(b) $y=|f(x)|$,
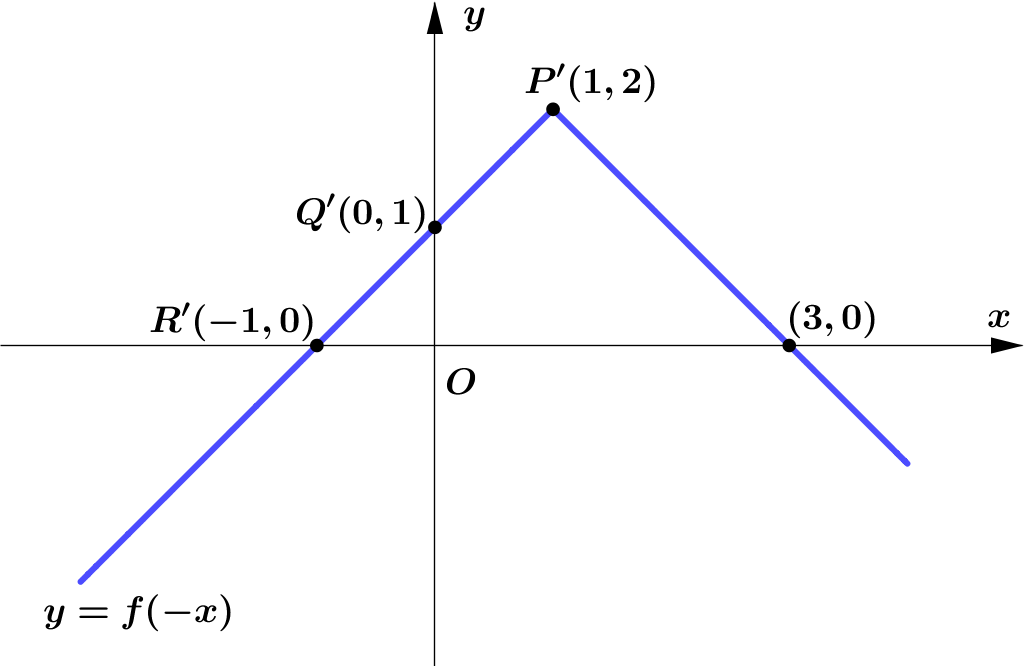
(c) $y=f(-x)$.
(d) Solve $f(x)=\dfrac{1}{2} x$.
SOLUTION
$\textbf{(a)} \quad$ $f(x)=2-|x+1|$
$P$ is the vertex of the graph $y=2-|x+1|$.
$\therefore\ $ The coordinate of the point $P$ is $(-1, 2)$.
$Q$ is the $y$-intercept of the graph $y=2-|x+1|$.
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\therefore\ \text{when } x&= 0\\\\
y&=2-|0+1|\\\\
&=1\\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\therefore\ $ The coordinate of the point $Q$ is $(0, 1)$.
$R$ is the positive $x$-intercept of the graph $y=2-|x+1|$.
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\therefore\ \text{when } y= 0\\\\
0 &=2-|x+1|\\\\
|x+1|&=2
x+1 &=\pm 2
\therefore\ x+1 &=-3 \text{ or } x&=1\\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\therefore\ $ The coordinate of the point $R$ is $(1, 0)$.
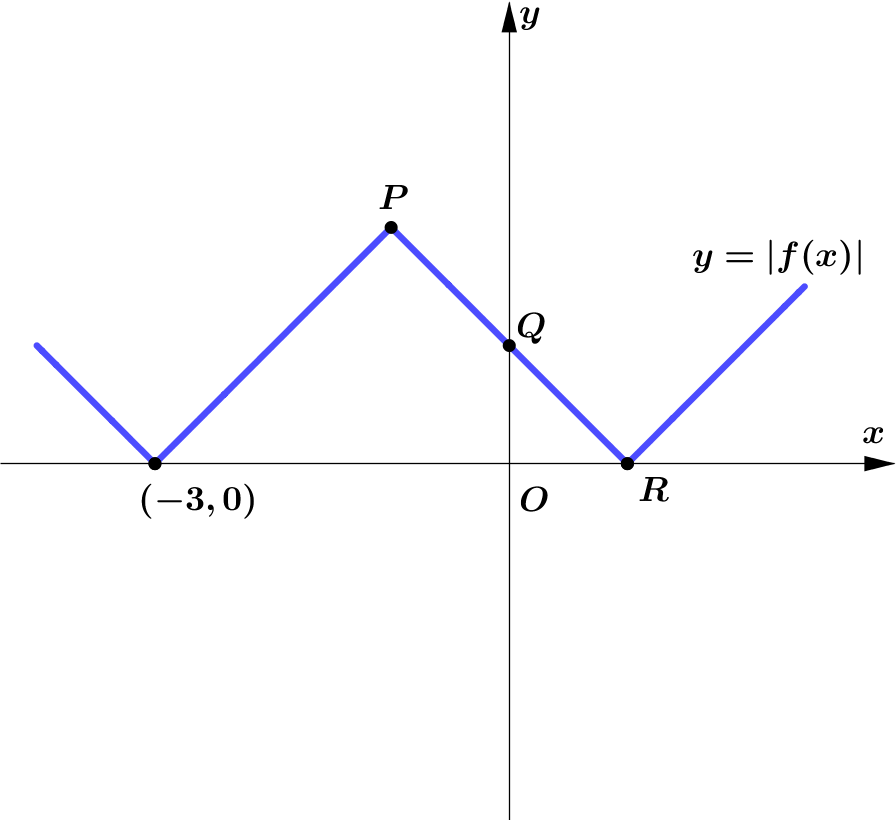
$\textbf{(b)} \quad$ On the graph $y=|f(x)|$,
All points are unchanged.
$\textbf{(c)} \quad$ On the graph $y=f(-x)$,
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\quad\quad &(-3, 0)\rightarrow (3, 0)\\\\
&(-1, 2)\rightarrow (1, 2)\\\\
&(0, 1)\rightarrow (0, 1)\\\\
&(1, 0)\rightarrow (-1, 0)\\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\textbf{(d)} \quad\quad f(x) &=\frac{1}{2} x \\\\
2-|x+1| &=\frac{1}{2} x \\\\
|x+1| &=2-\frac{1}{2} x \\\\
\therefore\ -(x+1) &=2-\frac{1}{2} x \ \text { or }\\\\
x+1&=2-\frac{1}{2} x \\\\
\therefore x &=-6 \ \text { or }\ x=\frac{2}{3}
\end{aligned}$
Question 4
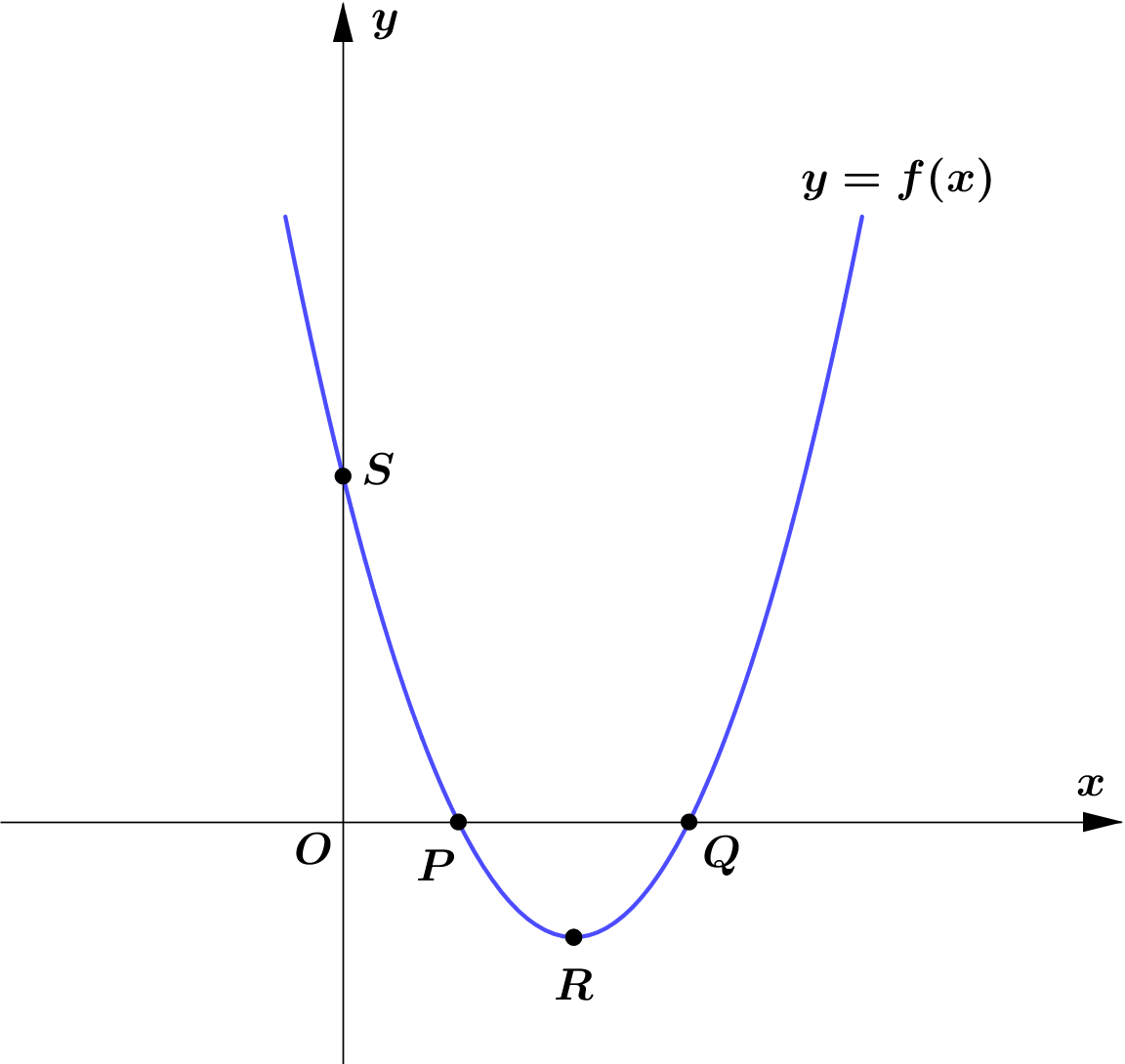
Given that $f(x)=(x-2)^2-1, x \in \mathbb{R}$.
Figure 4 shows the graph of $y=f(x)$.
$R$ is the vertex of the graph.The graph cuts the coordinate axes
at the points $P, Q$ and $S$.
(a) Find the coordinates of the points $P, Q, R$ and $S$.
(b) Sketch, the graph of $y=|f(x)|$ and $y=\dfrac{1}{2}(x-1)$ in the same plane.
(c) Hence or otherwise, find the the number of solutions of $|(x-2)^2-1|=\dfrac{1}{2}(x-1)$.
SOLUTION
$\textbf{(a)} \quad$ $f(x)=(x-2)^2-1$
$R$ is the vertex of the graph $y=(x-2)^2-1$.
$\therefore\ $ The coordinate of the point $R$ is $(2, -1)$.
$S$ is the $y$-intercept of the graph $y=(x-2)^2-1$.
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\therefore\ \text{when } x&= 0\\\\
y&=(0-2)^2-1\\\\
&=3\\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\therefore\ $ The coordinate of the point $S$ is $(3, 0)$.
$P$ and $Q$ are the $x$-intercepts of the graph $y=(x-2)^2-1$.
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\therefore\ \text{when } y= 0\\\\
0 &=y=(x-2)^2-1\\\\
(x-2)^2&=1
x-2 &=\pm 1
\therefore\ x=1 \text{ or } x&=3\\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\therefore\ $ The coordinate of the point $P$ and $Q$ are $(1, 0)$ and $(3, 0)$ respectively.
$\textbf{(b)} \quad$ On the graph $y=|f(x)|$,
Intercept points are unchanged.
The vertex is $R'(2,1)$.
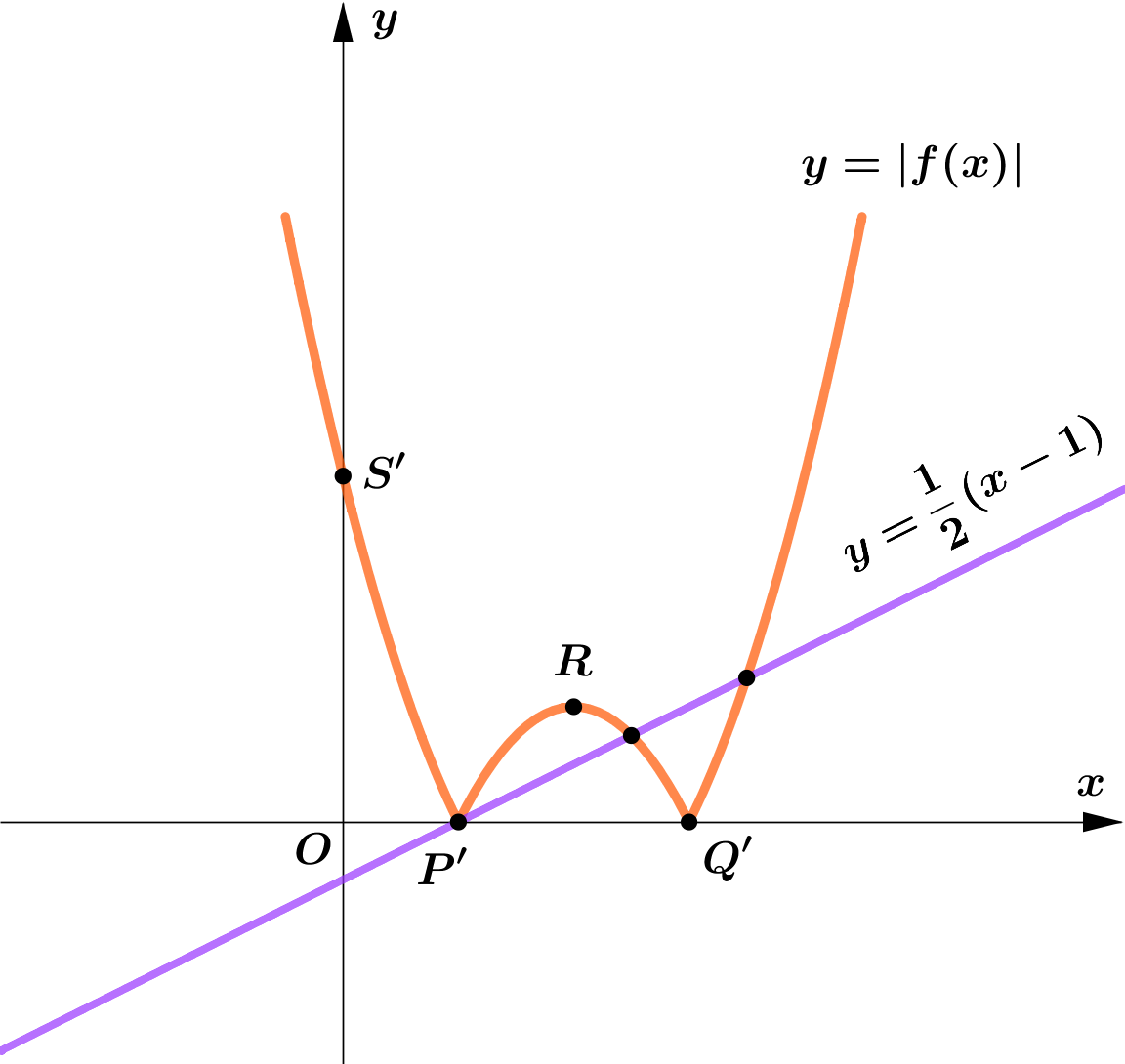
$\textbf{(c)} \quad$ According to the graph, there are three solutions
for the equation $|(x-2)^2-1|=\dfrac{1}{2}(x-1)$.
Question 5
The functions $f$ and $g$ are defined for all real values of $x$ by
$f(x)=3 x-2 \quad \text { and } \quad g(x)=3 x+7$
Find the exact coordinates of the point at which
(a) the graph of $y=(f\circ g)(x)$ meets the $x$-axis,
(b) the graph of $y=g(x)$ meets the graph of $y=g^{-1}(x)$,
(c) the graph of $y=|f(x)|$ meets the graph of $y=|g(x)|$.
SOLUTION
$\begin{aligned}
f(x) &=3 x-2 \\\\
g(x) &=3 x+7 \\\\
\left(f_{0} g\right)(x) &=f(g(x)) \\\\
&=f(3 x+7) \\\\
&=3(3 x+7)-2 \\\\
&=9 x+19\\\\
\end{aligned}$
When the graph of $y=(f \circ g)(x)$ meets the $x$-axis,
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
&9 x+19=0 \\\\
&x=-\frac{19}{9}\\\\
\end{aligned}$
The graph of $y=(f \circ g)(x)$ meets $x$-axis at $(-19 / 9, 0)$.
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
\text { Let } g^{-1}(x) &=p \\\\
g(p) &=x \\\\
3 p+7 &=x \\\\
p &=\frac{x-7}{3} \\\\
g^{-1}(x) &=\frac{x-7}{3}\\\\
\end{aligned}$
When $y=g(x)$ meets $y=g^{-1}(x)$,
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
3 x+7 &=\frac{x-7}{3} \\\\
9 x+2 &=x-7 \\\\
8 x &=-28 \\\\
x &=-\frac{7}{2} \\\\
\therefore\ y &=3\left(-\frac{7}{2}\right)+7 \\\\
&=-\frac{7}{2} \\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\therefore\ y =g(x)$ intersects y=g^{-1}(x)
at $\left(-\dfrac{7}{2},-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)$.
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
&y=|f(x)|=|3 x-2| \\\\
&y=|g(x)|=|3 x+7|\\\\
\end{aligned}$
When $y=|f(x)|$ meets $y=|g(x)|$,
$\begin{aligned}
&\\
|f(x)| &=|g(x)| \\\\
|3 x-2| &=|3 x+7| \\\\
3 x-2 &=-3 x-7 \text { or } 3 x-2=3 x+7 \\\\
6 x &=-5 \quad(\text { impossible) }\\\\
x &=-\frac{5}{6} \\\\
\therefore\ y &=\left|3\left(-\frac{5}{6}\right)-2\right|=\frac{9}{2}\\\\
\end{aligned}$
$\therefore$ The point of intersection of $y=|f(x)|$ and $y=|g(x)|$ is
$\left(-\dfrac{5}{6}, \dfrac{9}{2}\right)$.
Question 6
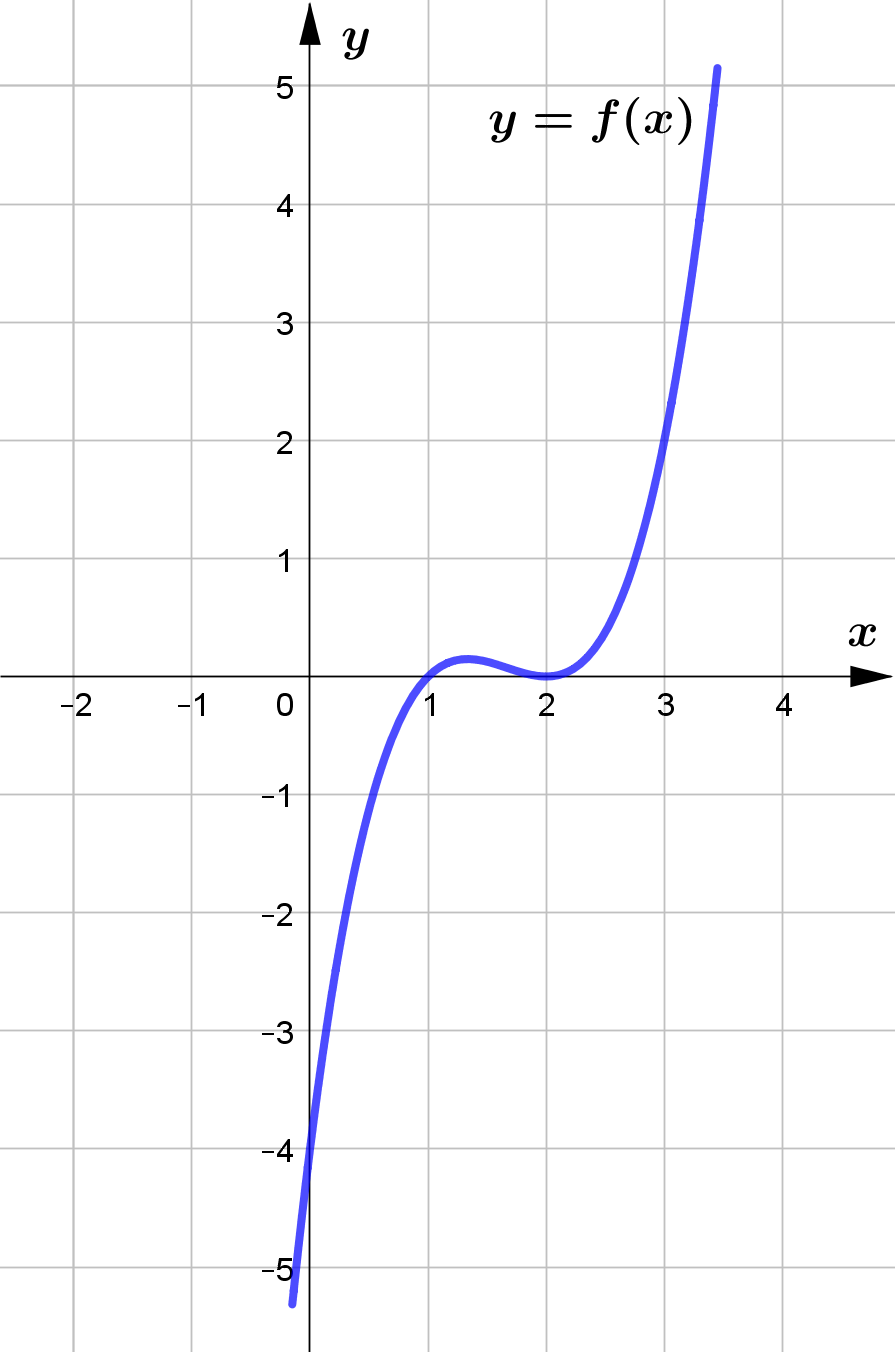
Given that $f(x)=(x-2)^2(x-1), x \in \mathbb{R}$.
Figure 5 shows part of the graph of $y=f(x)$.
(a) Sketch, the graph of $y=|f(x)|$ and $2x+3y=12$ in the same plane showing
the points of intersection of the two graphs.
(b) Hence or otherwise, find the solution set of the inequality
$|(x-2)^2(x-1)|\le 4-\dfrac{2}{3}x$.
SOLUTION
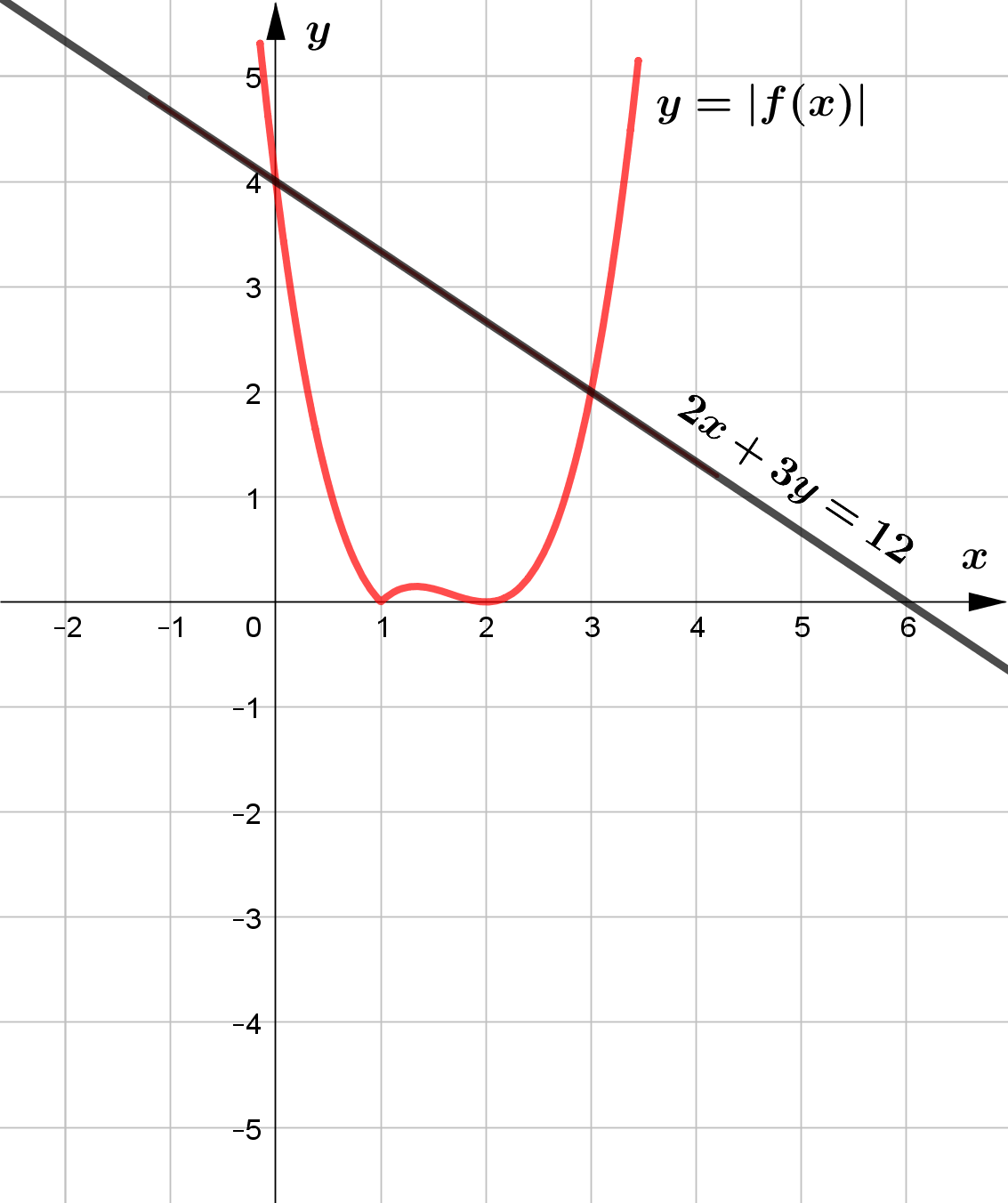
According to the graph the solution set of the inequality
$|(x-2)^2(x-1)|\le 4-\dfrac{2}{3}x$ is $\{x\mid 0\le x \le 3, x\in \mathbb{R}\}$

Post a Comment for "Graph of $y=|f(x)|$"